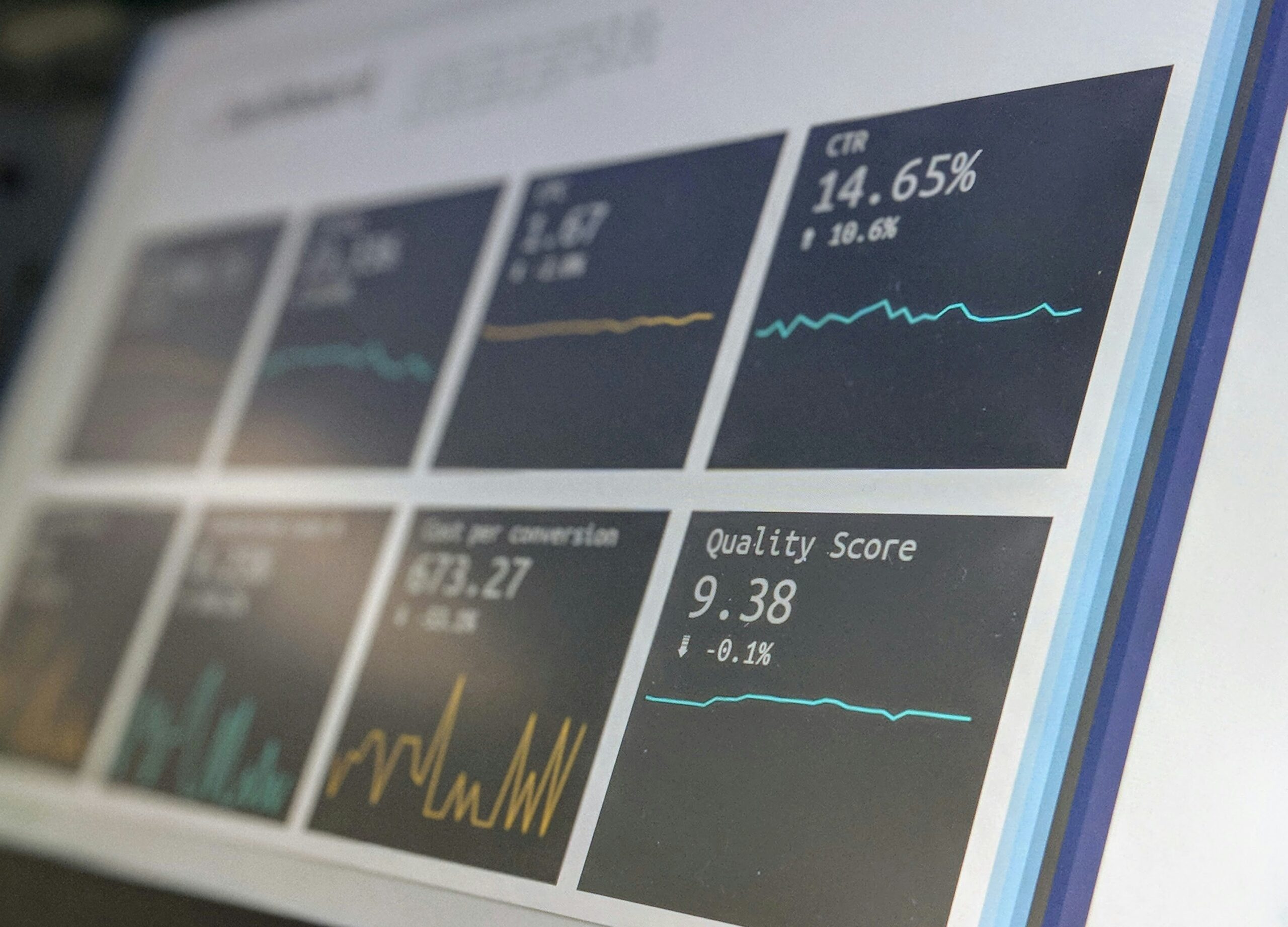
Introduction to Data Visualization
Data visualization refers to the graphical representation of information and data. By using visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization tools enable a more accessible interpretation of complex data sets. It plays a crucial role in data analysis by transforming raw data into an understandable visual context, allowing stakeholders to discern patterns, trends, and anomalies effectively.
The importance of data visualization cannot be overstated. In today’s data-driven world, organizations generate vast amounts of data daily. This influx poses the challenge of interpreting the information accurately and efficiently. Data visualization assists analysts and decision-makers in distilling intricate data into actionable insights. For example, presenting sales figures in a bar chart can reveal performance trends that may be obscured in traditional spreadsheets.
Beyond facilitating analysis, effective data visualization enhances communication. Visual representations of data are generally easier for audiences to comprehend than textual descriptions. For businesses, this means that insights can be shared more effectively across teams and management levels, fostering collaborative decision-making. Clients and stakeholders also benefit from clearer presentations that translate data points into narratives that drive understanding.
In addition to the clear value of visualization, leveraging specialized software tools enhances the process significantly. Such tools typically provide robust functionalities for creating interactive visualizations, simplifying the integration of various data sources, and offering real-time reporting capabilities. The increase in accessibility and user-friendliness of modern data visualization software means that even those without a background in data analysis can create meaningful visual insights. This democratization of data is essential for fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making across organizations.
Key Features to Look for in Data Visualization Software
When selecting data visualization software, there are several essential features that users should consider to ensure they choose a tool that meets their specific needs. Among the most critical factors is ease of use. A software solution that has a user-friendly interface allows both novice and experienced users to navigate the platform with minimal difficulty. This attribute is particularly important for organizations where not all personnel may possess advanced technical skills.
Flexibility is another crucial feature to evaluate. The best data visualization tools should be capable of accommodating various data sources and types. Users should look for software that can integrate effortlessly with databases, spreadsheets, and cloud applications. This capability ensures that teams can leverage existing data without facing compatibility issues, thereby improving overall workflow efficiency.
Customization options also play a vital role in the selection process. A good data visualization platform should offer diverse templates and the ability to create bespoke visualizations tailored to the user’s requirements. Such customization aids in delivering clearer insights specific to the audience, enhancing the effectiveness of data presentations.
Furthermore, integration capabilities with other tools and software applications are essential. Organizations often rely on multiple platforms for data management, and seamless integration between these tools allows users to create a more cohesive data analysis environment.
Finally, real-time reporting functionalities enhance the software’s value, enabling users to make informed decisions based on the most current data. This feature is particularly beneficial in fast-paced business environments where timely insights can significantly impact performance.
In summary, when evaluating data visualization tools, ease of use, flexibility, integration capabilities, customization options, and real-time reporting functionalities should be prioritized. These key features play a crucial role in ensuring that the selected software effectively meets the organization’s data visualization and reporting needs.
Top Software Options for Data Visualization
In the competitive landscape of data visualization software, several options stand out due to their robust features, user-friendliness, and adaptability to various business needs. Understanding the unique selling points of these tools can greatly assist organizations in selecting the best fit for their requirements.
Tableau is often regarded as a leader in the field of data visualization and reporting. Its powerful analytics capabilities allow users to create interactive and shareable dashboards easily. Tableau’s strength lies in its ability to handle large datasets, making it particularly suitable for enterprises requiring in-depth data analysis. Moreover, its extensive library of visualizations and strong community support enhances its usability, appealing to data analysts, business intelligence professionals, and organizations that prioritize data-driven decision-making.
Another significant contender is Power BI, developed by Microsoft. Its seamless integration with other Microsoft products, such as Excel and Azure, makes it a convenient choice for businesses already utilizing Microsoft ecosystems. Power BI stands out with its affordability and the capacity for real-time data visualization, which enriches reporting processes. Its interface is user-friendly, thus allowing users at various skill levels to create complex reports and dashboards effortlessly. It is particularly attractive to small to medium-sized enterprises looking to improve their data analytics without significant investments.
Google Data Studio provides a cloud-based solution that is favored for its accessibility and collaborative features. Its straightforward drag-and-drop interface enables users to create visually appealing reports quickly. Google Data Studio is especially advantageous for teams that rely heavily on other Google Suite applications and seek a cost-effective option as it is free of charge. Its target user group includes freelancers, marketing professionals, and small teams aiming for shared insights across platforms.
In summary, selecting the right software for data visualization and reporting hinges on understanding each tool’s capabilities and aligning them with the specific needs of the business. Whether it is Tableau’s comprehensive analytics, Power BI’s integration capabilities, or Google Data Studio’s collaborative features, each of these software options brings unique advantages to the table, ensuring organizations can effectively leverage their data.
Comparative Analysis of the Best Software
The marketplace offers a variety of software solutions for data visualization and reporting, each catering to different user needs and organizational capabilities. This analysis focuses on key aspects such as pricing, ease of use, performance, scalability, and support, which are essential when evaluating the best data visualization tools.
Pricing is a fundamental consideration. Many tools adopt subscription-based models, while others offer one-time purchase options. Tools like Tableau and Power BI provide tiered pricing, which allows organizations to choose plans that align with their budget and usage requirements. In contrast, open-source solutions, such as Apache Superset or Grafana, often have no direct costs, appealing to those with limited financial resources.
Ease of use is critical; tools with intuitive interfaces significantly reduce the learning curve for new users. Power BI is often lauded for its user-friendly design, enabling users with minimal technical expertise to create compelling visualizations rapidly. On the other hand, software like D3.js, while powerful, requires more programming knowledge, which may deter non-technical users.
Performance is another vital aspect, particularly when dealing with large datasets. Solutions like Looker have demonstrated the ability to handle substantial data volumes efficiently, while others, such as Google Data Studio, may encounter limitations as data size increases.
Scalability cannot be overlooked; as organizations expand, their data visualization tools must adapt seamlessly. Software like Tableau has proven robust in scaling with enterprise-level requirements, making it a favorite among large organizations. Moreover, support services strongly influence a software’s usability, and vendors that provide comprehensive documentation, forums, and customer service generally receive favorable reviews.
A comparison table can summarize these aspects, assisting users in making informed decisions about the software that best meets their data visualization needs.
Case Studies: Success Stories Using Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization software serves as a powerful tool for organizations aiming to enhance reporting processes and facilitate data analysis. Numerous case studies highlight the transformative impact that these tools can have across various industries. One notable example is a multinational retail corporation that utilized data visualization to optimize its supply chain management. By implementing a dashboard that displayed real-time inventory levels combined with sales trends, the company improved its operational efficiency, reducing excess stock by 20%. This not only minimized holding costs but also increased the responsiveness of inventory management to market demands.
Another compelling case is that of a healthcare organization that adopted data visualization tools to analyze patient outcomes. By integrating data from electronic health records and visualizing trends in patient recovery rates, the organization was able to identify areas needing improvement. This led to the development of targeted intervention strategies, ultimately resulting in a 15% increase in patient satisfaction scores. The clarity brought by data visualization allowed healthcare professionals to base their decisions on clear, visual insights rather than complex data sets.
Moreover, a financial services firm implemented a data visualization platform that provided dashboards for its analysts to monitor market trends and customer behavior. This initiative enabled the team to detect patterns and anomalies in data swiftly, enhancing their decision-making processes. The impact was significant, as the company experienced a 30% improvement in time-to-insight, which, in turn, led to more informed strategic decisions and better customer service outcomes.
The aforementioned examples illustrate the myriad ways that data visualization software can enhance reporting and data analysis across diverse sectors. By translating data into intuitively understandable visuals, organizations can unlock valuable insights, leading to enhanced decision-making and improved business performance.
Challenges and Limitations of Data Visualization Tools
While data visualization tools offer substantial benefits for interpreting complex data sets, users may encounter several challenges that can hinder their effectiveness. One significant challenge is data management. As organizations grow, the volume of data increases, and managing this data becomes more critical. Users may struggle with data integration from multiple sources, resulting in incomplete or inaccurate visualizations. Ensuring data cleanliness and consistency is vital for effective reporting, yet it is often a labor-intensive process.
Another challenge lies in the learning curve associated with these tools. Many data visualization platforms are robust, offering a wide range of features designed to enhance user experience. However, these advanced functionalities can often be overwhelming for new users. A steep learning curve may prevent quicker adoption of the tools and inhibit organizations from fully leveraging their capabilities. Proper training and support systems become essential in overcoming this hurdle, yet investing in such resources can entail additional costs for businesses.
Additionally, while data visualization is a powerful approach to convey insights, it has its limitations. Interpreting visual data can be complex, as users might misinterpret charts or graphs without a solid understanding of the underlying data. This complexity can lead to erroneous conclusions, prompting decision-makers to act on misleading information. Another concern is the risk of over-visualization; excessive use of graphics or overly intricate designs can clutter reports and obscure the main message, rather than highlight key insights. Thus, it is crucial for data professionals to strike a balance between informative and visually appealing representations.
In conclusion, while data visualization tools are invaluable assets, understanding the challenges and limitations associated with them is critical for maximizing their potential and ensuring accurate interpretations of data.
Best Practices for Effective Data Visualization
Effective data visualization is a fundamental component of data analysis and reporting. Utilizing best practices in creating visual representations can greatly enhance understanding and communication of insights derived from data. One crucial aspect is selecting the most appropriate chart types for the specific data being represented. Bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts serve different purposes and should be chosen based on the nature of the data and the story it aims to convey. For instance, line graphs are particularly effective for showcasing trends over time, while bar charts offer clarity for comparing discrete categories.
Color choices play a significant role in data visualization as well. It is important to use colors that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also meaningful. Utilizing contrasting colors can help distinguish different data sets within the same chart, while maintaining a consistent color palette throughout the visualizations aids in establishing a cohesive narrative. Additionally, it is advisable to avoid excessive use of bright colors, as they may distract viewers or distort the actual message of the visualization.
Labeling is another pivotal element that should not be overlooked. Clear, concise labels for axes, legends, and titles can significantly enhance the comprehension of the visualization. Labels should be easy to read and positioned logically to avoid confusion. Furthermore, including data values directly on or near the visual elements when appropriate can facilitate quicker comprehension and improve communication.
Finally, simplifying data presentations is vital for effective visualizations. Complex visualizations with excessive data can overwhelm the audience, leading to confusion. Strive to distill the core message into a clear and understandable format, ensuring that unnecessary details are omitted. By following these best practices for data visualization, individuals can create compelling visual narratives that facilitate a better understanding of the data and enhance the communication of insights.
Future Trends in Data Visualization and Reporting Software
The landscape of data visualization and reporting software is experiencing rapid evolution, driven largely by advancements in technology such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These innovative tools are significantly transforming how organizations process and interpret data. One of the most notable trends is the integration of AI capabilities that allow for automatic data analysis and visualization generation. This not only reduces the manual input required but also enhances the accuracy of insights derived from complex datasets.
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being utilized to identify patterns and trends within vast volumes of data, facilitating predictive analytics. This functionality enables organizations to foresee potential outcomes and make data-driven decisions with greater confidence. As machine learning becomes more sophisticated, we can anticipate that future data visualization tools will offer enhanced predictions and deeper insights, tailored specifically to users’ needs.
Another emerging trend is the focus on interactivity within data visualizations. Modern users demand more engaging and intuitive experiences, leading to the development of dynamic visualization tools. These tools allow users to interact with data in real-time, providing them with customized views and the ability to manipulate data on-the-fly. Such interactivity not only enhances user understanding but also promotes collaboration, as stakeholders can explore data together and derive insights cooperatively.
Furthermore, as the demand for advanced reporting capabilities grows, we are likely to see a rise in the usage of cloud-based data visualization solutions. These platforms offer scalability, real-time collaboration, and easy access from multiple devices, making them ideal for organizations looking to streamline their reporting processes. In conclusion, the future of data visualization and reporting software is set to be defined by enhanced AI capabilities, machine learning advancements, and increasingly interactive platforms. Organizations that adapt to these trends will be better positioned to leverage their data for strategic decision-making.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In the realm of data analysis, the selection of appropriate data visualization software is a critical step that can significantly influence the effectiveness of reporting and decision-making procedures. The right tools not only enhance interpretability but also facilitate the communication of complex data insights through intuitive visual formats. As discussed throughout this guide, various software options present different strengths such as integration capabilities, user-friendliness, and customization features. Consequently, practitioners must carefully align their requirements with the functionalities offered by these tools.
Among the leading data visualization software available today, options like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio emerged as particularly robust choices. Tableau is renowned for its sophisticated capabilities that cater to both novices and advanced users, while Power BI stands out due to its seamless integration with Microsoft products. Meanwhile, Google Data Studio continues to gain traction for its accessibility and collaborative features. Each of these platforms offers valuable resources, tutorials, and support systems to aid users in maximizing their data visualization practices.
When selecting software, it is prudent to consider aspects such as the type of data you’ll be visualizing, your budget, and whether you require real-time data analysis. Additionally, exploring user reviews and case studies can also provide insights into the experiences of others in a similar position, which may help inform your decision-making process. As data visualization continues to evolve, staying up-to-date with advanced features and emerging trends is essential. For those seeking to delve deeper into data visualization tools, numerous online communities, webinars, and workshops are available, providing valuable opportunities for skill enhancement and networking.